01.上了大学才知道,两个天天在一起的人不一定是朋友
02.上了大学才知道,从来不要和别人争论什么,因为那
03.上了大学才知道,手机是有事的时候用的,并不是为
04.上了大学才知道,真心对一个人好不一定有回报,而
05.上了大学才知道,很多东西是可遇而不可求的,很多
06.上了大学才知道,恋爱不一定是真心的,有可能是利
07.上了大学才知道,原来中学老师教的是那么好,那么
08.上了大学才知道,很多时候自己遇到不开心事,千万
09.上了大学才知道,有很多东西是不属于你的,你使劲
10.上了大学才知道,生活是有很多不公平的,你一定要
11.上了大学才知道,人的性格可以差异到如此之大。
12.上了大学才知道,一个人要自己对自己好,因为真正
13.上了大学才知道,课程会在你不经意间,拉下很多,
14.上了大学才知道,钱用的是那么快,用钱的地方是那
15.上了大学才知道,从现在开始应该把握每一个你能把
16.上了大学才知道,自己一定在乎自己的自尊,因为你
17.上了大学才知道,不要心情不好的时候对周围人发脾
18.上了大学才知道。即便有人对情感看的无所谓,你一
19.上了大学才知道,会遇到许多自己看不惯的人或事,
20.上了大学才知道,许多曾经的人会变的让你认不出,
21.上了大学才知道,会遇到很多诱惑,无论别人怎么样
22.上了大学才知道,会有人很讨厌你或者和你过不去,
23.上了大学才知道,很多人无法理解男女之间的朋友关
24.上了大学才知道,学习要刻苦,因为凭聪明就能应付
25.上了大学才知道,原来时间一空闲下来是那么无聊,
26.上了大学才知道,太在乎别人了往往会伤害自己。
27.上了大学才知道,对自己好的人会随着时间的流逝越
28.上了大学才知道,可以不把所有人当朋友,但千万不
29.上了大学才知道,玩你能玩的起的,玩不起的千万别
30.上了大学才知道,快乐常常来自回忆,而痛苦常常来
31.上了大学才知道,原来上课,吃饭,上自习常常得自
32.上了大学才知道,有很多人的想法与做法你无法理解
33.上了大学才知道,每个人都是带有“地方特色”的。
34.上了大学才知道,别人请客吃饭或着自己请别人吃饭
35.上了大学才知道,每个人都是认为自己的家乡最好,
關於榮辱觀的小故事十二生肖
有一次,我有機會和歐洲貴族聚餐。
可能酒喝多了,一位德國貴族站了起來,
諷刺說 : " 你 們中國人都是屬什麼豬啊!狗啊!老鼠啊!
不像我們,都是金牛座、獅子座、仙女座
……真不知道你們祖先怎麼想的? "
當時這些貴族聽完哈哈大笑,還互相碰杯,先前的優雅完全不見了。
按理說,人家在罵你祖宗了,你即使沒有話說,起碼可以掀桌子啊!
但所有人都坐著不吭聲,也可能是還沒反應過來,
我當時只好平和地告訴在場所有外賓:
"中 國人的祖先是很實在的,我們十二生肖 兩兩 相對,六道輪迴,
體現了我們祖先對中國人全部的期望跟要求。
" 這時 ,現場氣氛雖然從嬉鬧轉為安靜
,但是他們臉上還是一副不屑的樣子。
我說 :

" 第一組是老鼠和牛。老鼠代表智慧,牛代表勤奮。
智慧和勤奮一定要緊緊結合在一起。
如果光有智慧不勤奮,那就變成小聰明;而光是勤奮,不動腦筋,那就變成愚蠢。
所以這兩者一定要結合,這是我們祖先對中國人的第一組期望和要求,也是最重要的一組。

""第二組是老虎和兔子。老虎代表勇猛,兔子代表謹慎。
勇猛和謹慎一定要緊緊結合在一起,才能做到所謂的膽大心細。
如果勇猛離開了謹慎,就變成了魯莽,
而你沒有勇猛,一味的謹慎,謹慎就變成膽怯。
這一組也非常重要,所以放在第二。 "
我看著這些貴族,補上一句:
" 所以當我們表現出謹慎的時候,千萬不要以為我們中國人沒有勇猛的一面。我們祖先追求的是一種和諧的智慧和圓融,從來不會單獨給一個要求和任務。" 看著大家陷入沉思,我繼續往下說 。

"第三組是龍和蛇。龍代表剛猛,蛇代表柔韌。
所謂剛者易折,太剛了容易折斷,但是如果只有柔的一面,就易失去主見,所以剛柔並濟是我們歷代的祖訓。" 

接下來是馬和羊。馬代表勇往直前,直奔目標,羊代表和順 。如果一個人只顧自己直奔目標,不顧周圍,必然會和周圍不斷磕碰,最後不見得能達到目標。
但是一個人如果光顧著和周圍和順,之後他 連方向都沒有了,目標也失去了。 所以一往無前的秉性一定要與和順緊緊結合在一起,這是我們祖先對中國人的第四組期望。

" 再接下來是猴子和雞。猴子代表靈活,至於雞呢,
以前的年代沒有鐘,都是聽雞鳴聲決定一天的開始,所以雞定時打鳴,代表穩定。 靈活和穩定一定要緊緊結合起來。
如果你光靈活,沒有穩定,再好的政策最後也得不到收穫。但如果說你光是穩定,一潭死水、一塊鐵板,那就不會有我們今天的改革開放了。只有它們之間非常圓融的結合,一方面具有穩定性,保持整體的和諧和秩序,另一方面又能不斷變通地前進,這才是最根本的要旨。

" 最後是狗和豬 。狗是代表忠誠,豬是代表隨和。
一個人如果太忠誠,不懂得隨和,就會排斥他人。 而反過來,一個人太隨和,沒有忠誠,這個人就失去原則。
所以無論是對一個民族國家的忠誠、對團隊的忠誠,還是自己理想的忠誠,一定要與隨和緊緊結合在一起,這樣才容易真正保持內心深處的忠誠。
這就是我們 中國 人一直堅持的外圓內方,君子和而不同。
" 中國人每個 人都有屬於自己的生肖,有的人屬豬,有的人屬狗,這意義何在?實際上,我們的祖先期望我們要圓融,不能偏頗,要求我們懂得到對應面切入。比如屬豬的人能夠在他的隨和本性中,也去追求忠誠;而屬狗的人則在忠 誠的本性中,去做到隨和。"
解釋完十二生肖,我 說: " 不知道你們那些寶瓶座啊、射手座啊、公羊座啊,體現了你們祖先哪些期望和要求?也希望不吝賜教。 "
結果呢,
這些貴族老爺們很長時間都沒說話,全場鴉雀無聲,一根針掉在地上都能聽見。
最後貴族們紛紛由衷地表示對中國人和中國人的祖先非常敬佩:
" 沒有想到中國的十二生肖有這麼深刻而實在的意義。
女孩问男孩:[你还爱我吗]
男孩笑了,说[当然啦`小傻瓜`]
女孩笑得好不得意,说[那...你会爱我多久呢?]
男孩稍稍思索了一下,说[一辈子就够了.我会用我的一辈子爱你,直到我不能爱了.]
女孩仍不依不侥,又问[真的吗?那你用什么证明给我看!]
男孩想了想,拉起女孩的手向外走.
女孩不明白,问男孩[你要带我去哪?]
男孩一直都不说,只是紧紧地拉着女孩的手,一直走,穿过喧闹的大街,他们来到一间别致的小店.
女孩忍不住好奇心,又问了[这是哪啊?]
男孩拉着女孩的手,走进了店里.
男孩说[我要在这里,证明,我真的会爱你一辈子的!]
原来,这里是一家专给纹身的店铺,男孩让店员给他们俩分别在左手无名指的地方都纹了一枚漂亮的4叶草.
男孩轻轻抱着女孩,伏在她耳边说道[亲爱哒`现在我们手上的4叶草就像两枚戒指一样,而且是永远也摘不掉了!这样,就不怕以后我会离开你了,除非..我这只手指断掉了,或者说,我死了...]
女孩赶紧用手捂住男孩的嘴,说[猪啊!我知道了,我知道你一定不会离开我的!不准你死!你要是死了,谁来给我欺负捏`嘿嘿`]
男孩把女孩抱得更紧了.[好,我不死.我就一辈子给你欺负喽`谁叫我就是爱你呢`呵呵`亲爱哒老婆!]
[谁是你老婆了`哼`]
[你就是,你都戴了我的戒指了!不许赖账的!]
[哼`我要砍了它!]
[你敢!]男孩的心突然纠得紧紧的.
[我...不敢!嘿嘿`]
.................
从那以后,男孩和女孩一直感情很好,偶尔女孩任性,男孩总是让着她.
女孩曾经暗暗发誓,她要跟这个男孩一辈子,不离不弃!
可是有一天....
男孩突然对女孩说[我们分手吧.]
女孩吓了一大跳,捉着男孩的手,问[为什么!]
男孩说[一起久了,开始腻了.]
女孩无法接受,她不能没有他!
女孩说[你不是说过要爱我一辈子的吗?难道你都忘了吗?还有,我们,我们的4叶草,我们的4叶草戒指啊!这个是永远也弄不掉了的,你怎么可以丢下我~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
男孩一面淡漠,毫无感情地说道[这个可以去掉的...我会想办法去掉的.]
[为什么!那我们以前的一切都要去掉么?你怎么可以这么狠心`]女孩无可抑止地大叫起来.
[我..我还是走了.]男孩转身要走.
[不要!不要离开我!]女孩紧紧拉着男孩的手,但男孩一用力便把她给甩开了.
男孩走了,女孩终于忍不住痛哭起来.
她看着左手无名指上的戒指,看了好久,好久,难道幸福真的只是假像么?
..............
第二天,男孩收到女孩的来信.
就容许我最后一次这样叫你吧.
昨天,你走之后,我想了好多好多,我想到我们的从前.从前我们多开心,多幸福啊.
曾经听朋友说过这样一句话:如果开始回忆,那现在就已经开始受伤.
是吧,昨天,你真的伤得我好深,知道吗?我好痛,真的好痛...
你亲手杀死了我们的爱情,就那样走掉,就留下我一个人处理,善后么?你说你会让那枚4叶草去掉,但是我做不到啊!我无法埋葬我们的爱情,我们地过去,我..我只能埋葬自己....
其实,我真的不能没有你.
我一直都不相信有真爱,是你让我看到;我一直不信有幸福,是你让我感受到;我一直不相信有永远,你证明给我看.可是这一切难道都是假的吗?怎么可以都忘了,我却还一直记得啊.我忘不掉啊`
失去你,我真的不知道还要怎么过下去,以后的日子,只有我自己一个人的日子...
那,就让我最后任性一次吧..我离开,离开这个让我好痛好痛的地方...
男孩看完信,双手颤抖得厉害,他...怎么能这样伤害一个自己深爱的女孩?
男孩疯了一般跑到女孩的家里,可迎来的却是一片白....
女孩已经飞走了,飞回她原来的天堂....
男孩跪倒在女孩冰凉的尸体前,泣不成声....
作者: Regina Brett,90歲,來自俄亥俄州,克里夫蘭,Plain Dealer城
他說:為了慶祝變得更老了,我曾經寫下人生教我的45個功課。這是我寫過最叫座的專欄。
我這把老骨頭8月就要90歲了,所以,再一次,在這裡呈現這一個專欄。
1。 人生是不公平,但還是好得很。
2。 懷疑的時候,為未來踏出一小步。
3。 人生太短,短到來不及浪費時間去恨任何一個人。
4。 生病的時候,你的工作不會照顧妳。你的朋友和父母會。保持聯絡。
5。 每一個月付清你的信用卡。
6。 你不需要每一次都吵贏。同意你不同意的。
7。 找人一起哭。它比獨自啜泣更加療愈。
8。 對上帝生氣沒有關係。祂受得了。
9。 退休存款從你的第一張薪水條開始。
10。講到巧克力,抗拒只是徒勞無功。
11。和你的過去和解,所以它不會搞砸你的當下。
12。讓你的孩子看到你哭沒有關係。
13。別拿自己的人生和他人做比較。你根本不清楚他們的人生是怎麼一回事。
14。如果一段親密關係要偷偷摸摸,你根本不應該涉入。
15。一眨眼的功夫什麼都會變。但是別擔心: 上帝從來不眨眼。
16。深吸一口氣。它會安定你的腦。
17。沒用,不美,或不喜悅的東西都丟掉。
18。沒讓你死的真的會讓你更堅強。
19。重拾快樂童年永不嫌晚。但這第二次只能靠你不靠人。
20。當關乎追求你生命的所愛,不要把不要當答案。
21。點蠟燭,用好的床單,穿上炫麗的內衣。不要特殊場合才用。今天就是特別的一天。
22。準備要過於周全,然後隨遇而安。
23。現在就離經叛道。不要一把年紀了才開始穿上紫色。
24。最重要的性器官是腦袋。
25。除了你,沒有人在主宰你的快樂。
26。把所謂的不幸用這一句話把它表框起來 "五年後,這還重要嗎?"
27。永遠選擇生活。
28。原諒每一個人每一件事。
29。別人怎麼看你不干你的事。
30。時間會痊癒幾乎每一件事。要給時間,時間。
31。無論情況多好或多壞,它都會變的。
32。不要那麼認真的看待自己。沒有人會這樣看待你的。
33。相信奇蹟。
34。上帝愛你是因為祂就是這樣,不是因為你做了什麼或是沒做什麼。
35。不要稽查人生。現在就呈現和做最大的發揮。
36。變老了打敗另一種選項 - 死得早。
37。你的孩子只有一個童年。
38。最後真正最重要的是你愛過。
39。每一天都出門。奇蹟在四處等著。
40。如果我們都把我們的問題都丟成一堆,然後看看其他人的,我們會把我們的撿回來。
41。忌妒浪費時間。你已經擁有你所需要的了。
42。最好的都還沒來。
43。不管你感覺如何,起來,穿好和呈現。
44。讓自己每天快樂。
45。人生不會打上蝴蝶結,但它仍然是一份禮物。
These are all the recipes on this site in alphabetical order. I must thank one of my readers, Angeline, who took time to write to me and giving me this suggestion. Since it is a good suggestion, I have worked on it (it’s tedious by the way!) and hope this page will serve as an easy reference for the recipes here. Non-recipe posts such as Food Reviews and Miscellaneous musings are not included here for obvious reasons.
Introduction
Programmable controllers are generally programmed in ladder diagram (or "relay diagram") which is nothing but a symbolic representation of electric circuits. Symbols were selected that actually looked similar to schematic symbols of electric devices, and this has made it much easier for electricians to switch to programming PLC controllers. Electrician who has never seen a PLC can understand a ladder diagram.
Ladder diagram
There are several languages designed for user communication with a PLC, among which ladder diagram is the most popular. Ladder diagram consists of one vertical line found on the left hand side, and lines which branch off to the right. Line on the left is called a "bus bar", and lines that branch off to the right are instruction lines. Conditions which lead to instructions positioned at the right edge of a diagram are stored along instruction lines. Logical combination of these conditions determines when and in what way instruction on the right will execute. Basic elements of a relay diagram can be seen in the following picture.

Most instructions require at least one operand, and often more than one. Operand can be some memory location, one memory location bit, or some numeric value -number.In a case when we wish to proclaim a constant as an operand, designation # is used beneath the numeric writing (for a compiler to know it is a constant and not an address.)
Based on the picture above, one should note that a ladder diagram consists of two basic parts: left section also called conditional, and a right section which has instructions. When a condition is fulfilled, instruction is executed, and that's all!

Picture above represents a example of a ladder diagram where relay is activated in PLC controller when signal appears at input line 0. Vertical line pairs are called conditions. Each condition in a ladder diagram has a value ON or OFF, depending on a bit status assigned to it. In this case, this bit is also physically present as an input line (screw terminal) to a PLC controller. If a key is attached to a corresponding screw terminal, you can change bit status from a logic one status to a logic zero status, and vice versa. Status of logic one is usually designated as "ON", and status of logic zero as "OFF".
Right section of a ladder diagram is an instruction which is executed if left condition is fulfilled. There are several types of instructions that could easily be divided into simple and complex. Example of a simple instruction is activation of some bit in memory location. In the example above, this bit has physical connotation because it is connected with a relay inside a PLC controller. When a CPU activates one of the leading four bits 10, relay contacts move and connect lines attached to it. In this case, these are the lines connected to a screw terminal marked as 0 and to one of COM screw terminals.
Normally open and normally closed contacts
Since we frequently meet with concepts "normally open" and "normally closed" in industrial environment, it's important to know them. Both terms apply to words such as contacts, input, output, etc. (all combinations have the same meaning whether we are talking about input, output, contact or something else).
Principle is quite simple, normally open switch won't conduct electricity until it is pressed down, and normally closed switch will conduct electricity until it is pressed. Good examples for both situations are the doorbell and a house alarm.
If a normally closed switch is selected, bell will work continually until someone pushes the switch. By pushing a switch, contacts are opened and the flow of electricity towards the bell is interrupted. Of course, system so designed would not in any case suit the owner of the house. A better choice would certainly be a normally open switch. This way bell wouldn't work until someone pushed the switch button and thus informed of his or her presence at the entrance.
Home alarm system is an example of an application of a normally closed switch. Let's suppose that alarm system is intended for surveillance of the front door to the house. One of the ways to "wire" the house would be to install a normally open switch from each door to the alarm itself (precisely as with a bell switch). Then, if the door was opened, this would close the switch, and an alarm would be activated. This system could work, but there would be some problems with this, too. Let's suppose that switch is not working, that a wire is somehow disconnected, or a switch is broken, etc. (there are many ways in which this system could become dysfunctional). The real trouble is that a homeowner would not know that a system was out of order. A burglar could open the door, a switch would not work, and the alarm would not be activated. Obviously, this isn't a good way to set up this system. System should be set up in such a way so the alarm is activated by a burglar, but also by its own dysfunction, or if any of the components stopped working. (A homeowner would certainly want to know if a system was dysfunctional). Having these things in mind, it is far better to use a switch with normally closed contacts which will detect an unauthorized entrance (opened door interrupts the flow of electricity, and this signal is used to activate a sound signal), or a failure on the system such as a disconnected wire. These considerations are even more important in industrial environment where a failure could cause injury at work. One such example where outputs with normally closed contacts are used is a safety wall with trimming machines. If the wall doors open, switch affects the output with normally closed contacts and interrupts a supply circuit. This stops the machine and prevents an injury.
Concepts normally open and normally closed can apply to sensors as well. Sensors are used to sense the presence of physical objects, measure some dimension or some amount. For instance, one type of sensors can be used to detect presence of a box on an industry transfer belt. Other types can be used to measure physical dimensions such as heat, etc. Still, most sensors are of a switch type. Their output is in status ON or OFF depending on what the sensor "feels". Let's take for instance a sensor made to feel metal when a metal object passes by the sensor. For this purpose, a sensor with a normally open or a normally closed contact at the output could be used. If it were necessary to inform a PLC each time an object passed by the sensor, a sensor with a normally open output should be selected. Sensor output would set off only if a metal object were placed right before the sensor. A sensor would turn off after the object has passed. PLC could then calculate how many times a normally open contact was set off at the sensor output, and would thus know how many metal objects passed by the sensor.
Concepts normally open and normally closed contact ought to be clarified and explained in detail in the example of a PLC controller input and output. The easiest way to explain them is in the example of a relay.
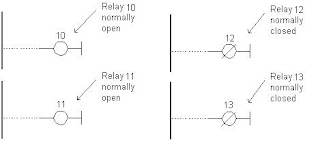
Normally open contacts would represent relay contacts that would perform a connection upon receipt of a signal. Unlike open contacts, with normally closed contacts signal will interrupt a contact, or turn a relay off. Previous picture shows what this looks like in practice. First two relays are defined as normally open , and the other two as normally closed. All relays react to a signal! First relay (10) has a signal and closes its contacts. Second relay (11) does not have a signal and remains opened. Third relay (12) has a signal and opens its contacts considering it is defined as a closed contact. Fourth relay (13) does not have a signal and remains closed because it is so defined.
Concepts "normally open" and "normally closed" can also refer to inputs of a PLC controller. Let's use a key as an example of an input to a PLC controller. Input where a key is connected can be defined as an input with open or closed contacts. If it is defined as an input with normally open contact, pushing a key will set off an instruction found after the condition. In this case it will be an activation of a relay 0.
If input is defined as an input with normally closed contact, pushing the key will interrupt instruction found after the condition. In this case, this will cause deactivation of relay 0 (relay is active until the key is pressed). You can see in picture below how keys are connected, and view the relay diagrams in both cases.

Normally open/closed conditions differ in a ladder diagram by a diagonal line across a symbol. What determines an execution condition for instruction is a bit status marked beneath each condition on instruction line. Normally open condition is ON if its operand bit has ON status, or its status is OFF if that is the status of its operand bit. Normally closed condition is ON when its operand bit is OFF, or it has OFF status when the status of its operand bit is ON.
When programming with a ladder diagram, logical combination of ON and OFF conditions set before the instruction determines the eventual condition under which the instruction will be, or will not be executed. This condition, which can have only ON or OFF values is called instruction execution condition. Operand assigned to any instruction in a relay diagram can be any bit. This means that conditions in a relay diagram can be determined by a status of I/O bits, operational bits, timers/counters, etc.
Malaysia Weather - Tropical year round climate
With an equatorial climate, Malaysia weather sees high temperatures year round with humidity levels at around 90%. This can feel stifling in the major urban areas such as Kuala Lumpur but coastal beach resorts do enjoy cooling afternoon breezes. Rainfall can occur at any time but is more pronounced on the east coast in winter months with the onset of monsoon winds. Daytime temperatures throughout the year rarely drop below 30c with 7-8 hours of daily sunshine. The many inland hill stations have cooler, fresher air quality with extremely pleasant temperatures and mild evenings.
Weather in Malaysia - Consistent hot and dry summers
The summer months are hot and dry with a small possibility of rain which is usually brief. Temperatures can reach 34c but this is often tempered by cooling sea breezes particularly during June and July. The sun typically shines for 8 hours each day and inland, higher altitude resorts are popular with tourists and locals alike as they seek relief from the heat and humidity. The states of Sabah and Sarawak in Malaysian Borneo are more prone to variable weather. Surrounded by South East Asia's highest peak and dense rainforest this region can become wetter and overcast in summer but is in general still hot and sultry.
Malaysia weather - Cool and refreshing at altitude
Weather in Malaysia has two distinct periods of wet weather characterised by incoming monsoon winds. East coast peninsular Malaysia and Malaysian Borneo suffer the heaviest downpours during winter months which can be accompanied by high winds or thunderstorms. From November to February diving on the east coast islands become less rewarding with lower visibility and shipping can sometimes be affected. Despite this, temperatures remain high at 30c with sunny skies for 6 hours a day. Malaysia weather offers a good year round climate ideal for a beach holiday, rarely disrupted by the weather and pleasantly cool temperatures at altitude.

















